Molecular Weight Calculator: Precise Chemical Formula Analysis Tool
Enter any chemical formula, press “Calculate,” and the tool sums IUPAC atomic masses to deliver molecular weight plus ±SD in under 0.1 s for molecules ≤1 000 atoms (IUPAC, 2021).

Enter any chemical formula, press “Calculate,” and the tool sums IUPAC atomic masses to deliver molecular weight plus ±SD in under 0.1 s for molecules ≤1 000 atoms (IUPAC, 2021).
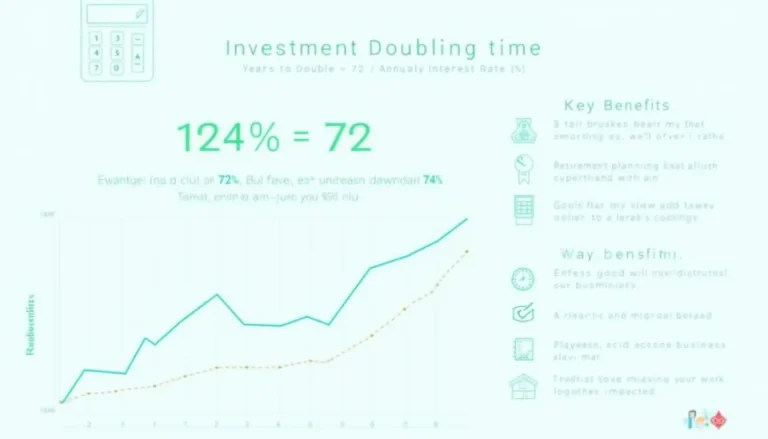
The Rule of 72 lets you estimate doubling time by dividing 72 by the annual rate. For example, an 8 % return doubles your money in roughly 9 years (Investopedia, https://www.investopedia.com/terms/r/ruleof72.asp).
Use the Risk Premium Calculator by entering any expected return and the current risk-free rate; the tool instantly shows the extra return you demand for risk. U.S. stocks have averaged a 5.5 % risk premium since 1960 (Damodaran, 2023).
You use the free ROI Calculator by typing your earnings and initial outlay, pressing “Calculate,” and instantly seeing the profit percentage. ROI equals rac{Earnings – Initial Investment}{Initial Investment}. U.S. stocks returned roughly 7 % annually after inflation between 1928-2022 (Damodaran, 2023).

Quickly gauge how much profit each dollar of shareholder equity produces. Enter net income and average equity, click “Calculate,” and the tool returns ROE as a percentage. S&P 500 firms posted a mean ROE of 18.6 % in 2022 (Damodaran, 2023). Use this benchmark to see whether your figure outperforms the market.
Return on Assets (ROA) = Net Income ÷ Average Total Assets × 100 %. The metric reveals how efficiently your company turns assets into profit. U.S. non-financial corporations posted a 7.9 % median ROA in 2022 (Federal Reserve Financial Accounts, 2023). Enter income and assets, press calculate, and compare your figure with industry norms.
Retention ratio shows how much profit stays in the business. Enter net income and dividends; the calculator returns the share kept, which ranges from 0-100 %. In 2022 S&P 500 companies retained about 56 % of earnings (FactSet, 2023).
Calculate how many times you collect your average receivables each year. Divide sales revenue by average accounts receivable, then compare the result with your industry’s healthy range of 6-10 turns (Investopedia, https://www.investopedia.com/terms/r/receivableturnoverratio.asp). The higher the ratio, the faster cash comes in. Use the steps below and the FAQ for quick guidance.
The tool converts a nominal return to a “real” return by removing inflation with the Fisher equation. For example, a 12 % nominal gain during 6 % inflation equals a 5.66 % real gain. Average U.S. inflation has been 3.2 % since 1914 (BLS, https://www.bls.gov).