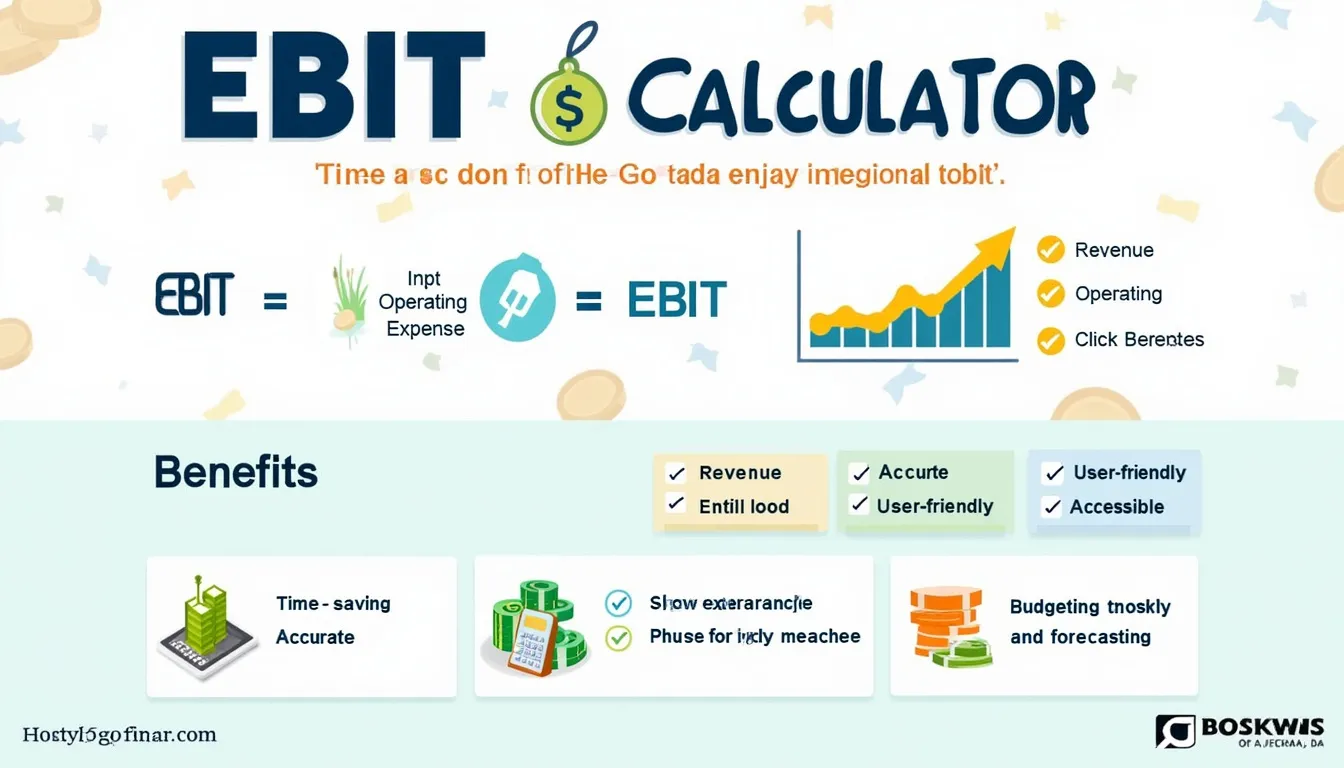
Interest Coverage Ratio Calculator
Is this tool helpful?
How to use the tool
- Revenue (USD) – type your total sales. Example inputs: 1 350 000 or 975 000.
- Cost of Goods and Services (USD) – enter direct production costs. Examples: 820 000 or 640 000.
- Operating Expenses (USD) – add administrative, selling, and general costs. Examples: 290 000 or 180 000.
- Interest Expense (USD) – record total interest paid on debt. Examples: 75 000 or 42 000.
- Press “Calculate” to display Earnings Before Interest and Taxes (EBIT) and the Interest-Coverage Ratio.
Formulas used
$$ \text{EBIT}= \text{Revenue}-\text{Cost of Goods and Services}-\text{Operating Expenses} $$ $$ \text{Interest Coverage Ratio}= \frac{\text{EBIT}}{\text{Interest Expense}} $$
Worked example
- Revenue: $1 800 000
- Cost of Goods and Services: $1 050 000
- Operating Expenses: $400 000
- Interest Expense: $150 000
EBIT calculation: $$ 1\,800\,000-1\,050\,000-400\,000 = 350\,000 $$
Interest-Coverage calculation: $$ \frac{350\,000}{150\,000}=2.33 $$
The company earns 2.33 × its interest cost, showing moderate coverage.
Quick-Facts
- Coverage ≥ 3 × is generally considered healthy (Moody’s, 2021).
- S&P 500 industrial firms averaged 6 × in 2022 (S&P Global Market Intelligence, 2023).
- Loan covenants often require a minimum of 2 × (Federal Reserve Senior Loan Officer Survey, 2023).
- IFRS defines borrowing costs in IAS 23 for interest calculations (IFRS Foundation, 2022).
FAQ
What is the interest-coverage ratio?
The ratio shows how many times EBIT can pay current interest charges, revealing debt-service safety (Investopedia, 2023).
Why does the ratio matter?
Lenders and rating agencies use it to gauge default risk; low values increase borrowing costs (S&P Global, 2023).
What counts as a “good” ratio?
Most analysts want ≥ 3 ×; utilities can pass at 2 ×; airlines need nearer 4 × (Moody’s, 2021).
Can the ratio be negative?
Yes—negative EBIT yields a negative ratio and signals severe operating losses (SEC Form 10-K Guide, 2023).
How often should you calculate it?
Quarterly reviews align with financial statements and expose trend shifts early (PwC Financial Reporting Manual, 2023).
Does it affect credit ratings?
“Interest-coverage is a primary indicator of financial endurance” (S&P Criteria, 2019). Higher ratios boost ratings.
How can you improve your ratio?
Raise prices, cut discretionary costs, refinance at lower rates, or retire high-interest debt (Deloitte Debt Advisory, 2023).
Is a very high ratio always positive?
Extremely high coverage can mean under-leveraging and missed growth financed cheaply (Harvard Business Review, 2022).
Important Disclaimer
The calculations, results, and content provided by our tools are not guaranteed to be accurate, complete, or reliable. Users are responsible for verifying and interpreting the results. Our content and tools may contain errors, biases, or inconsistencies. Do not enter personal data, sensitive information, or personally identifiable information in our web forms or tools. Such data entry violates our terms of service and may result in unauthorized disclosure to third parties. We reserve the right to save inputs and outputs from our tools for the purposes of error debugging, bias identification, and performance improvement. External companies providing AI models used in our tools may also save and process data in accordance with their own policies. By using our tools, you consent to this data collection and processing. We reserve the right to limit the usage of our tools based on current usability factors.