Heart Rate Calculator
Is this tool helpful?
How to Use the Heart Rate Calculator Effectively
Our Heart Rate Calculator is a powerful tool designed to help you monitor and understand your cardiovascular health. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to use it effectively:
1. Enter the Number of Beats Counted
In the first field, input the number of heartbeats you counted during your measurement. For example, if you counted 18 beats, enter “18” in this field.
2. Specify the Time Interval
Next, enter the duration over which you counted the beats in seconds. Common intervals are 15, 30, or 60 seconds. For instance, if you counted for 15 seconds, enter “15” in this field.
3. Input Your Age
Enter your current age in years. This information is crucial for calculating your maximum heart rate. For example, if you’re 30 years old, enter “30” in the age field.
4. Provide Your Resting Heart Rate (Optional)
If you know your resting heart rate, enter it in beats per minute (bpm). This value is typically measured first thing in the morning before getting out of bed. For instance, if your resting heart rate is 60 bpm, enter “60” in this field. If you don’t know your resting heart rate, you can leave this field blank.
5. Select Your Desired Intensity Level
Choose the exercise intensity level you’re aiming for from the dropdown menu. Options include:
- Light (50-60% of Maximum Heart Rate)
- Moderate (60-70% of Maximum Heart Rate)
- Vigorous (70-85% of Maximum Heart Rate)
- Maximum (85-95% of Maximum Heart Rate)
6. Calculate and View Results
Click the “Calculate” button to process your inputs. The calculator will display your results, including:
- Calculated Heart Rate
- Maximum Heart Rate
- Target Heart Rate Zone
- Heart Rate Reserve
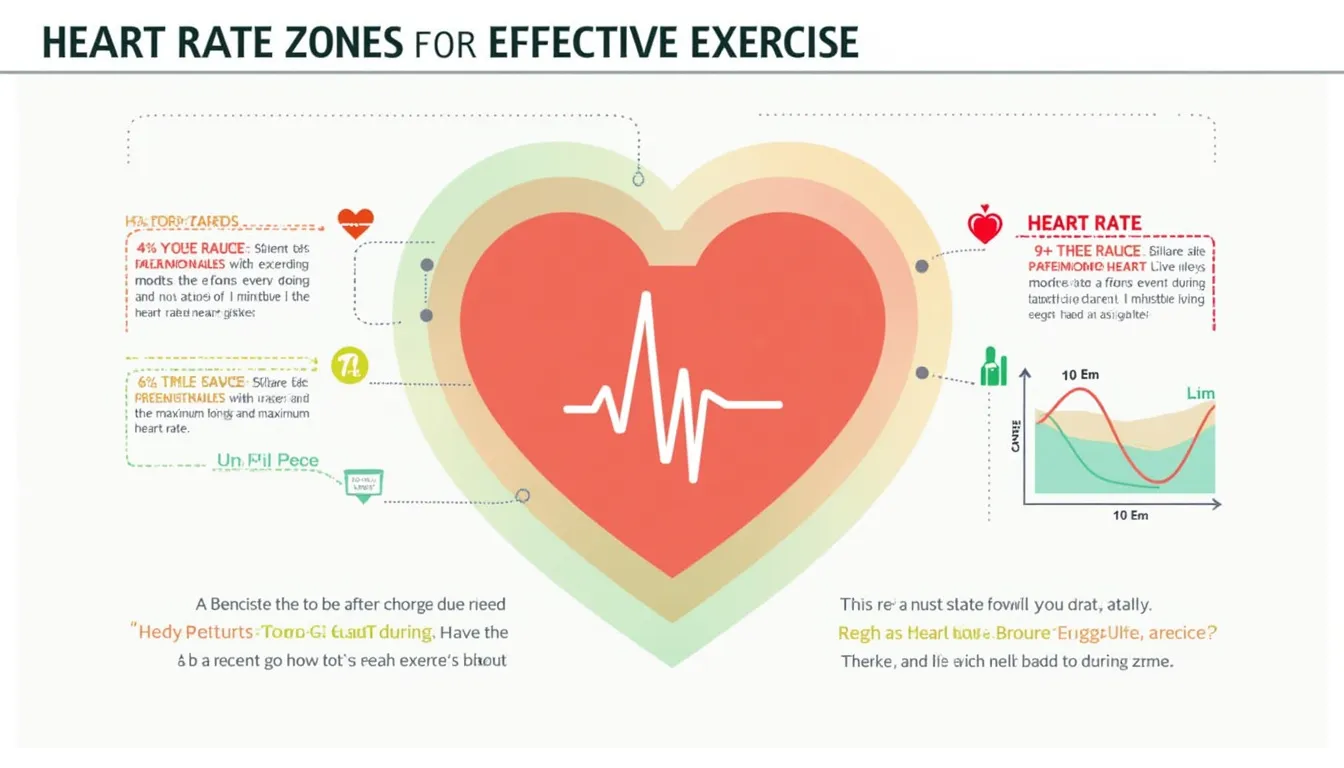
Understanding Your Heart Rate: A Comprehensive Guide
Heart rate is a vital sign that provides crucial information about your cardiovascular health and fitness level. It represents the number of times your heart beats per minute (bpm) and can vary significantly based on factors such as age, fitness level, activity, and overall health.
The Importance of Monitoring Heart Rate
Regularly tracking your heart rate offers numerous benefits:
- Assesses your overall cardiovascular health
- Helps optimize your workout intensity
- Monitors your fitness progress over time
- Aids in preventing overexertion during exercise
- Provides insights into stress levels and recovery
Types of Heart Rate Measurements
1. Resting Heart Rate (RHR)
Your resting heart rate is the number of times your heart beats per minute while you’re at complete rest. A lower RHR generally indicates better cardiovascular fitness. For most adults, a normal resting heart rate ranges from 60 to 100 bpm, with well-trained athletes often having RHRs as low as 40 to 60 bpm.
2. Maximum Heart Rate (MHR)
Maximum heart rate is the highest number of times your heart can beat in one minute. It’s primarily determined by age and can be estimated using the following formula:
$$MHR = 220 – Age$$3. Target Heart Rate Zones
Target heart rate zones are ranges of heart rates that correspond to different exercise intensities. These zones are typically calculated as percentages of your maximum heart rate:
- Light Intensity: 50-60% of MHR
- Moderate Intensity: 60-70% of MHR
- Vigorous Intensity: 70-85% of MHR
- Maximum Effort: 85-95% of MHR
Benefits of Using the Heart Rate Calculator
1. Personalized Fitness Guidance
By inputting your age and selecting your desired intensity level, our calculator provides personalized target heart rate zones. This information helps you tailor your workouts to achieve specific fitness goals, whether you’re aiming for weight loss, endurance improvement, or cardiovascular health.
2. Accurate Heart Rate Calculation
The calculator uses a precise formula to determine your current heart rate based on the number of beats counted and the time interval. This eliminates the need for manual calculations and reduces the risk of errors.
3. Maximum Heart Rate Estimation
Understanding your estimated maximum heart rate is crucial for safe and effective exercise. Our calculator provides this information based on your age, helping you avoid overexertion during workouts.
4. Heart Rate Reserve Calculation
For those who input their resting heart rate, the calculator determines your heart rate reserve (HRR). This value is useful for more advanced training methods and provides a more personalized approach to exercise intensity.
5. Easy Tracking of Fitness Progress
By regularly using the calculator, you can monitor changes in your heart rate over time. This allows you to track improvements in your cardiovascular fitness and adjust your training accordingly.
How the Heart Rate Calculator Addresses User Needs
Simplifying Complex Calculations
Our calculator takes the guesswork out of heart rate calculations. Instead of manually computing your heart rate or trying to remember complex formulas, you can simply input a few values and receive accurate results instantly.
Providing Personalized Exercise Guidance
By offering target heart rate zones based on your age and desired intensity level, the calculator helps you exercise at the right intensity for your goals. This personalized guidance can improve the effectiveness of your workouts and reduce the risk of overtraining or undertraining.
Enhancing Safety During Exercise
Knowing your maximum heart rate and appropriate target zones helps prevent overexertion during workouts. This is particularly important for beginners or those with health concerns who need to monitor their exercise intensity carefully.
Supporting Various Fitness Goals
Whether you’re aiming for weight loss, endurance building, or general health improvement, understanding your heart rate zones can help you tailor your workouts accordingly. For example:
- Fat burning: Focus on the moderate intensity zone (60-70% of MHR)
- Cardiovascular endurance: Target the vigorous intensity zone (70-85% of MHR)
- Recovery workouts: Stay within the light intensity zone (50-60% of MHR)
Facilitating Long-term Health Monitoring
Regular use of the heart rate calculator allows you to track changes in your resting heart rate and exercise heart rates over time. This can provide valuable insights into your improving cardiovascular fitness and overall health.
Practical Applications and Examples
Example 1: Calculating Current Heart Rate
Let’s say you counted 22 beats in 15 seconds. Here’s how the calculator would determine your current heart rate:
$$Heart Rate = (Number of Beats / Time Interval in Seconds) × 60$$ $$Heart Rate = (22 / 15) × 60 = 88 bpm$$Example 2: Determining Target Heart Rate Zones
For a 35-year-old individual aiming for moderate-intensity exercise:
- Calculate Maximum Heart Rate: $$MHR = 220 – 35 = 185 bpm$$
- Calculate Moderate Intensity Zone (60-70% of MHR): $$Lower Limit = 185 × 0.60 = 111 bpm$$ $$Upper Limit = 185 × 0.70 = 130 bpm$$
The calculator would suggest a target heart rate zone of 111-130 bpm for moderate-intensity exercise.
Example 3: Using Heart Rate Reserve for Personalized Zones
Consider a 40-year-old with a resting heart rate of 65 bpm, aiming for vigorous exercise (70-85% intensity):
- Calculate Maximum Heart Rate: $$MHR = 220 – 40 = 180 bpm$$
- Calculate Heart Rate Reserve (HRR): $$HRR = MHR – RHR = 180 – 65 = 115 bpm$$
- Calculate Target Heart Rate using Karvonen Formula: $$Target HR = [(MHR – RHR) × Intensity%] + RHR$$ $$Lower Limit = [(180 – 65) × 0.70] + 65 = 145 bpm$$ $$Upper Limit = [(180 – 65) × 0.85] + 65 = 163 bpm$$
The calculator would recommend a personalized vigorous intensity zone of 145-163 bpm.
Example 4: Tracking Fitness Progress
A user might record their resting heart rate weekly using the calculator. If their initial RHR was 72 bpm and after two months of regular exercise it decreased to 65 bpm, this indicates improved cardiovascular fitness.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: How often should I measure my resting heart rate?
A: It’s best to measure your resting heart rate first thing in the morning, before getting out of bed. Tracking it daily can provide the most accurate picture, but weekly measurements are sufficient for most people.
Q2: Can I use this calculator if I have a heart condition?
A: While the calculator can provide general guidance, individuals with heart conditions should consult their healthcare provider for personalized advice on heart rate monitoring and exercise intensity.
Q3: Why does my heart rate vary throughout the day?
A: Heart rate fluctuates naturally due to various factors including physical activity, emotional state, body position, hydration levels, and time of day. This is normal and not a cause for concern unless the variations are extreme or accompanied by other symptoms.
Q4: How can I lower my resting heart rate?
A: Regular cardiovascular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, managing stress, and getting adequate sleep can all contribute to lowering your resting heart rate over time.
Q5: Is it safe to exercise at my maximum heart rate?
A: Exercising at or near your maximum heart rate should only be done for short periods and by individuals in excellent physical condition. For most people, it’s safer and more beneficial to exercise within the moderate to vigorous intensity zones.
Q6: How accurate is the age-based maximum heart rate formula?
A: The 220 minus age formula provides a reasonable estimate for most people. However, individual variations exist, and some people may have higher or lower maximum heart rates than predicted.
Q7: Can medications affect my heart rate?
A: Yes, certain medications can influence heart rate. Beta-blockers, for example, can lower heart rate, while some stimulants may increase it. Always inform your healthcare provider about any medications you’re taking when discussing heart rate and exercise.
Q8: How long should I exercise in my target heart rate zone?
A: For general cardiovascular health, aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity exercise per week. This can be spread out over several sessions throughout the week.
Q9: What’s the difference between aerobic and anaerobic exercise in terms of heart rate?
A: Aerobic exercise typically occurs at 70-80% of your maximum heart rate, where your body can sustain the activity for extended periods. Anaerobic exercise pushes your heart rate above 80% of its maximum, and can only be sustained for short bursts.
Q10: How does altitude affect heart rate?
A: At higher altitudes, where oxygen levels are lower, your heart rate may increase both at rest and during exercise as your body works harder to deliver oxygen to your tissues. It’s important to adjust your exercise intensity accordingly when at high altitudes.
By understanding and regularly using this Heart Rate Calculator, you can take a more informed and scientific approach to your fitness journey. Whether you’re a beginner just starting to monitor your heart health or an experienced athlete fine-tuning your training, this tool provides valuable insights to help you achieve your health and fitness goals safely and effectively.
Important Disclaimer
The calculations, results, and content provided by our tools are not guaranteed to be accurate, complete, or reliable. Users are responsible for verifying and interpreting the results. Our content and tools may contain errors, biases, or inconsistencies. We reserve the right to save inputs and outputs from our tools for the purposes of error debugging, bias identification, and performance improvement. External companies providing AI models used in our tools may also save and process data in accordance with their own policies. By using our tools, you consent to this data collection and processing. We reserve the right to limit the usage of our tools based on current usability factors. By using our tools, you acknowledge that you have read, understood, and agreed to this disclaimer. You accept the inherent risks and limitations associated with the use of our tools and services.