Force Calculator
Is this tool helpful?
How to use the tool
- Mass field – Type any positive value, then pick kg, g, or lb.
Try 75 kg or 330 g. - Acceleration field – Enter the rate of change of velocity, then choose m/s² or ft/s².
Try 2.1 m/s² or 14 ft/s². - Preset – Skip manual entry by selecting Earth, Moon, Mars, or Jupiter gravity.
- Press “Calculate Force.” You instantly see force in newtons and pound-force, plus a trend-line graph.
Formula used
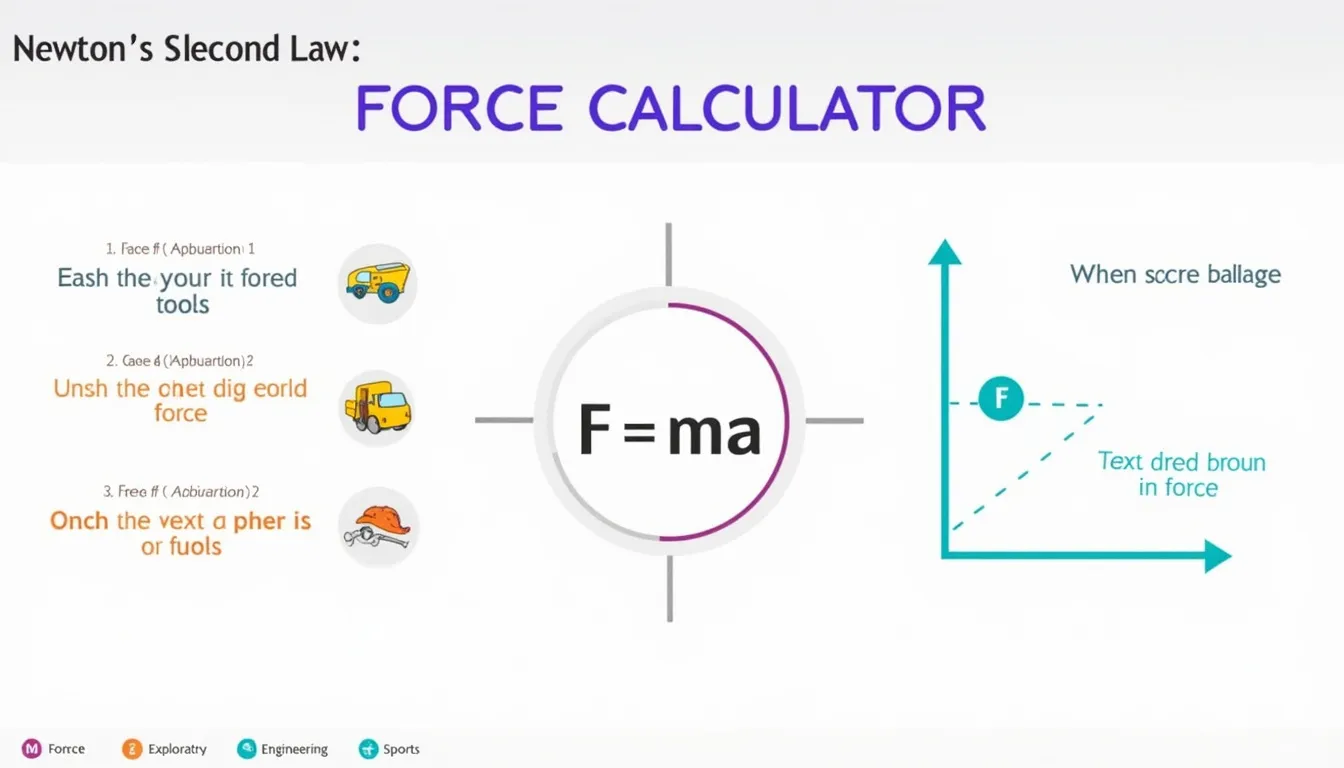
The calculator applies Newton’s Second Law:
$$F = m \times a$$
where F is force (N), m is mass (kg), and a is acceleration (m/s²).
Worked example 1
- Input: 75 kg, 2.1 m/s².
- Force: $$F = 75 \times 2.1 = 157.5\;\text{N}$$.
- Pound-force: $$157.5 \times 0.224809 = 35.4\;\text{lbf}$$.
Worked example 2
- Input: 330 g → 0.33 kg, 14 ft/s² → 4.267 m/s².
- Force: $$F = 0.33 \times 4.267 = 1.41\;\text{N}$$.
- Pound-force: $$1.41 \times 0.224809 = 0.32\;\text{lbf}$$.
Quick-Facts
- Newton’s Second Law: $$F = m·a$$ (Serway, 2020).
- Standard gravity: 9.80665 m/s² (CODATA, 2018).
- Conversion: 1 N = 0.224809 lbf (NIST, 2020).
- Moon gravity: 1.62 m/s² (NASA, 2022).
- Mars gravity: 3.71 m/s² (NASA, 2022).
FAQ
What does the calculator compute?
It multiplies mass by acceleration to output force in newtons and pound-force, following Newton’s Second Law (Serway, 2020).
How accurate are the unit conversions?
The tool uses CODATA constants and NIST 2019 conversion factors; numerical precision matches four decimal places (NIST, 2020).
Why offer pound-force as a second unit?
Pound-force is common in U.S. engineering; showing both units prevents errors during imperial-metric handoffs (ASME Y14.5-2018).
Can I enter values in grams?
Yes. The script divides grams by 1000 to obtain kilograms before calculating force, ensuring consistency with SI rules (ISO 80000-1:2009).
What range of masses is practical?
The interface accepts any positive number, yet typical lab tests run 0.01-500 kg for safe handling (NIST Mass Metrology Guide, 2021).
How do planetary presets work?
Choosing a planet inserts its surface gravity as acceleration, letting you compare weight differences instantly (NASA Planetary Fact Sheet, 2022).
Does the graph show real-time recalculations?
Yes. Submitting new data rebuilds the Chart.js line plot, updating twenty evenly spaced mass points across your entry.
Is the tool suitable for classroom demonstrations?
Absolutely. Quick visual feedback and unit flexibility align with STEM curriculum standards for kinematics labs (NGSS HS-PS2-1, 2013).
Important Disclaimer
The calculations, results, and content provided by our tools are not guaranteed to be accurate, complete, or reliable. Users are responsible for verifying and interpreting the results. Our content and tools may contain errors, biases, or inconsistencies. Do not enter personal data, sensitive information, or personally identifiable information in our web forms or tools. Such data entry violates our terms of service and may result in unauthorized disclosure to third parties. We reserve the right to save inputs and outputs from our tools for the purposes of error debugging, bias identification, and performance improvement. External companies providing AI models used in our tools may also save and process data in accordance with their own policies. By using our tools, you consent to this data collection and processing. We reserve the right to limit the usage of our tools based on current usability factors.