Cost of Equity Calculator
Is this tool helpful?
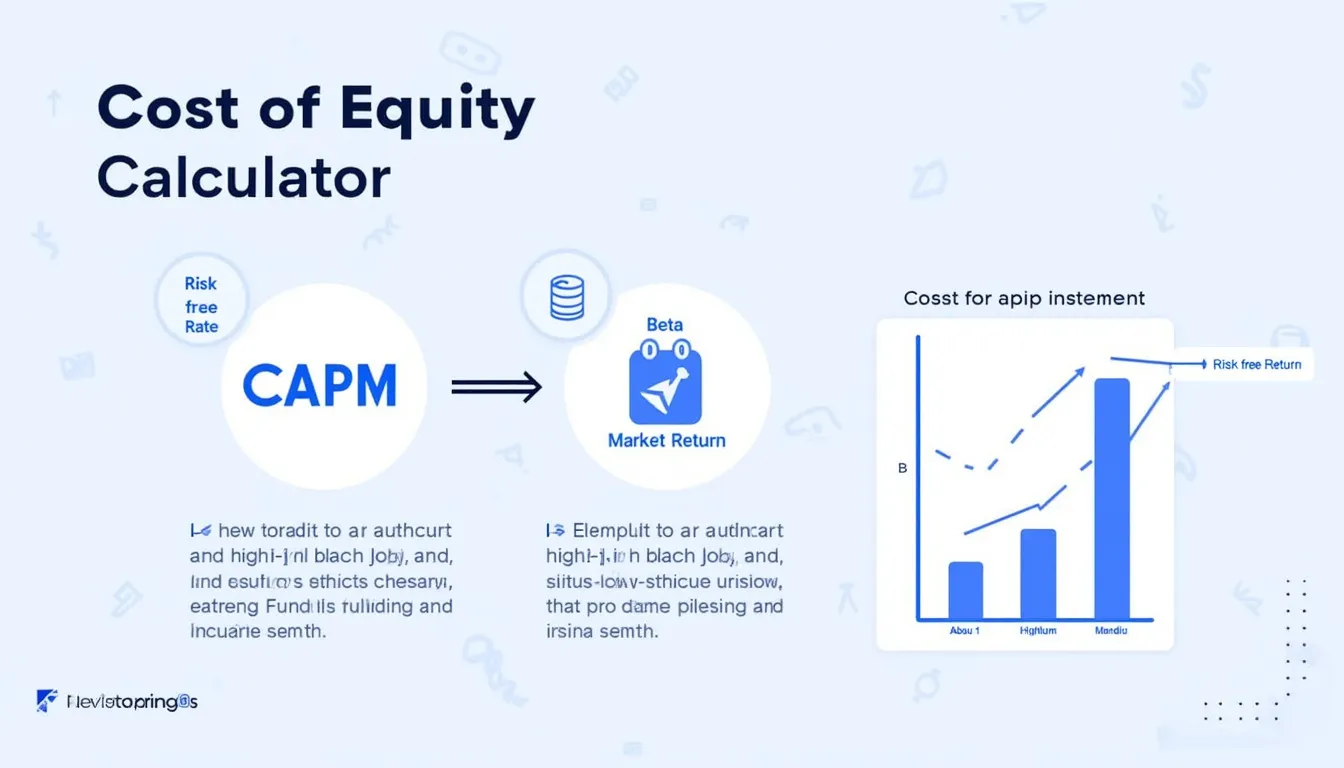
Enter a risk-free rate, beta and expected market return to instantly see your cost of equity via the CAPM formula. U.S. 10-year Treasury yield averaged 3.9 % in 2023 (U.S. Treasury, 2024).
How to use the tool
- Risk-free Rate (%) – type a current government-bond yield, such as 0.8 or 4.1. Non-negative values only.
- Beta – input the stock’s beta, e.g., 0.7 for low volatility or 1.8 for high volatility.
- Market Return (%) – add your expected broad-market return, like 5.6 or 10.2.
- Press “Calculate” to display your cost of equity instantly; the form validates every field before computing.
Formula used
The calculator applies the Capital Asset Pricing Model:
$$ \text{Cost of Equity}=R_f+\beta\,(R_m-R_f) $$Example
- Risk-free rate (R_f = 3.0,%)
- Beta (beta = 0.8)
- Market return (R_m = 9.0,%)
Calculation:
$$ 3.0 + 0.8\,(9.0 – 3.0)=3.0 + 0.8 \times 6.0 = 3.0 + 4.8 = 7.8\,\% $$Therefore, investors require a 7.8 % return to hold the equity under these assumptions.
Quick-Facts
- Typical beta for utility stocks ≈ 0.55 (Damodaran, 2024).
- Global equity risk premium averaged 5.6 % in 2023 (KPMG, 2023).
- Most analysts update WACC quarterly (CFA Institute, 2020).
- “Beta reflects only systematic risk” (Investopedia, Cost of Equity Definition).
FAQ
What is cost of equity?
Cost of equity is the return you must promise shareholders for the risk they accept (Investopedia, Cost of Equity Definition).
Why use the CAPM formula?
CAPM links expected return to market risk, providing a widely accepted benchmark for valuation (Sharpe, 1964).
Where can I find a reliable risk-free rate?
Use current yields on same-currency government bonds, e.g., U.S. 10-year Treasury on the Fed’s H.15 report (Federal Reserve, 2024).
How does beta affect the result?
Higher beta increases the ( beta(R_m-R_f) ) term, raising the cost of equity linearly (Damodaran, 2024).
Can cost of equity drop below the risk-free rate?
No; CAPM implies equality only when beta equals zero, which real equities rarely exhibit (CFA Institute, 2020).
How often should I recalculate?
Recalculate whenever market yields, beta estimates or growth assumptions change—minimum quarterly (KPMG, 2023).
Is beta stable over time?
Beta drifts with leverage and business changes; Bloomberg adjusts weekly using 2-year regressions (Bloomberg Terminal Guide, 2023).
What if my company is privately held?
Use industry-average beta, then relever for your target debt-equity ratio (Pratt & Grabowski, 2022).
Important Disclaimer
The calculations, results, and content provided by our tools are not guaranteed to be accurate, complete, or reliable. Users are responsible for verifying and interpreting the results. Our content and tools may contain errors, biases, or inconsistencies. We reserve the right to save inputs and outputs from our tools for the purposes of error debugging, bias identification, and performance improvement. External companies providing AI models used in our tools may also save and process data in accordance with their own policies. By using our tools, you consent to this data collection and processing. We reserve the right to limit the usage of our tools based on current usability factors. By using our tools, you acknowledge that you have read, understood, and agreed to this disclaimer. You accept the inherent risks and limitations associated with the use of our tools and services.